Schizophrenia
What is schizophrenia?
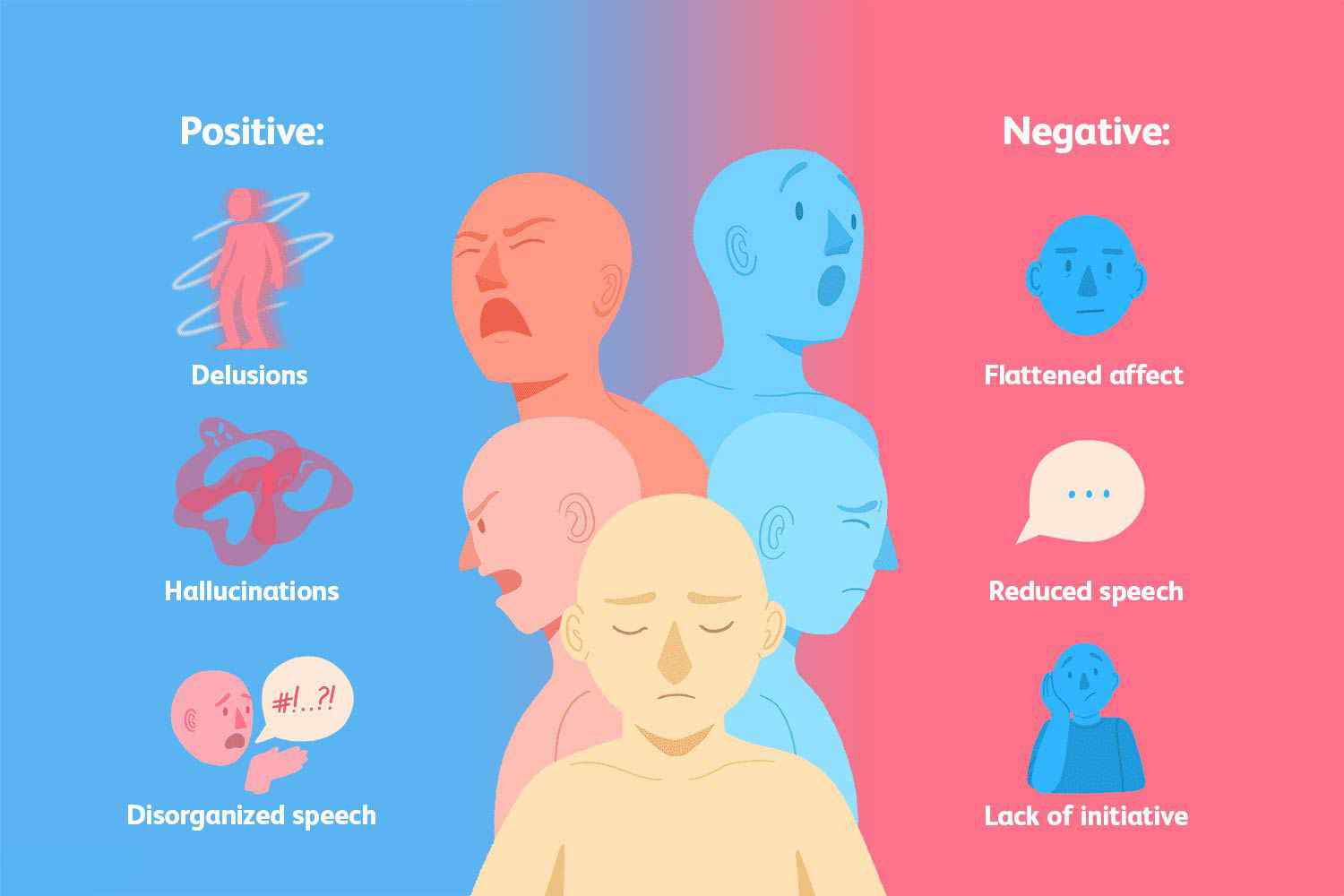
Schizophrenia is a chronic mental illness that affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves. People with schizophrenia may experience hallucinations (seeing or hearing things that aren't there), delusions (false beliefs), disorganized thinking, and problems with social interactions.
What are the symptoms of schizophrenia?
The symptoms of schizophrenia can vary from person to person, but they may include:
- Hallucinations: Seeing or hearing things that aren't there.
- Delusions: False beliefs that are not based in reality.
- Disorganized thinking: Difficulty thinking clearly or following a train of thought.
- Problems with social interactions: Difficulty understanding social cues or relating to others.
- Changes in mood: Feeling depressed, anxious, or irritable.
- Changes in behavior: Withdrawal from social activities, changes in sleep or eating patterns, or increased risk-taking behavior.
What causes schizophrenia?
The exact cause of schizophrenia is not fully understood, but it is thought to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some environmental factors that may contribute to schizophrenia include exposure to certain viruses or toxins during pregnancy, or experiencing a stressful life event.
How is schizophrenia treated?
There is no cure for schizophrenia, but there are treatments that can help manage the symptoms. The most common treatment for schizophrenia is medication, such as antipsychotics. Other treatments that may be helpful include therapy, social skills training, and support groups.
What is the prognosis for schizophrenia?
The prognosis for schizophrenia varies from person to person. Some people with schizophrenia may experience a full recovery, while others may have ongoing symptoms. However, with treatment, most people with schizophrenia can live relatively normal lives.
What is the difference between schizophrenia and psychosis?
Psychosis is a broad term that refers to a loss of contact with reality. Schizophrenia is a specific type of psychosis that is characterized by hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking.
What is the difference between schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder?
Schizoaffective disorder is a mental illness that shares some symptoms of schizophrenia and some symptoms of mood disorders, such as depression or bipolar disorder. People with schizoaffective disorder may experience hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking, as well as mood symptoms such as depression, mania, or both.
What is the difference between schizophrenia and personality disorder?
Personality disorders are a group of mental illnesses that are characterized by enduring patterns of thinking, feeling, and behaving. Schizophrenia is not a personality disorder, but some people with schizophrenia may also have a personality disorder.
If you are concerned that you or someone you know may have schizophrenia, it is important to see a doctor for evaluation. Early diagnosis and treatment can help improve the outcome for people with schizophrenia.